 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
SNMP Protocol Basic Request/Response Information Poll Using GetRequest and (Get)Response Messages
The obvious place to begin our detailed look at SNMP protocol operations is with the simplest type of information exchange. This would be a simple poll operation to read one or more management information variables, used by one SNMP entity (typically an SNMP manager) to request or read information from another entity (normally an SNMP agent on a managed device). SNMP implements this as a simple two-message request/response protocol exchange, similar the request/reply processes found in so many TCP/IP protocols.
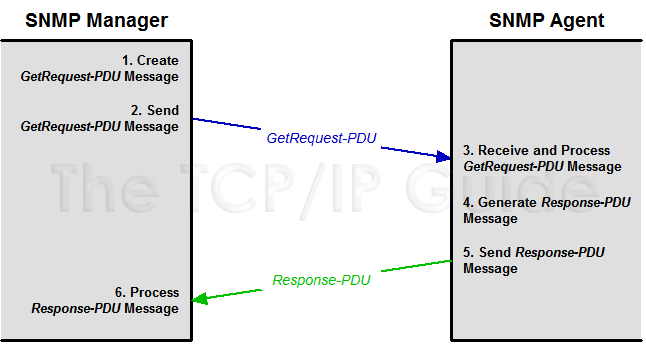
This information request process typically begins with the user of an application wanting to check the status of a device or look at information about it. As we've seen, all this information is stored on the device in the form of MIB objects. The communication, therefore, takes the form of a request for particular MIB objects and a reply from the device containing those objects' values. In simplified form, the steps in the process are as follows (and as shown in Figure 274):
- SNMP Manager Creates GetRequest-PDU:
Based on the information required by the application and user, the SNMP
software on the network management station creates a GetRequest-PDU
message. It contains the names of the MIB objects whose values the application
wants to retrieve.
- SNMP Manager Sends GetRequest-PDU:
The SNMP manager sends the PDU to the device that is being polled.
- SNMP Agent Receives and Processes
GetRequest-PDU: The SNMP agent receives and processes the
request. It looks at the list of MIB object names contained in the message
and checks to see if they are valid (ones the agent actually implements).
It looks up the value of each variable that was correctly specified.
- SNMP Agent Creates Response-PDU:
The agent creates a Response-PDU to send back to the SNMP Manager.
This message contains the values of the MIB objects requested and/or
error codes to indicate any problems with the request, such as an invalid
object name.
- SNMP Agent Sends Response-PDU:
The agent sends the response back to the SNMP Manager.
- SNMP Manager Processes Response-PDU:
The manager processes the information in the Response-PDU received
from the agent.
Figure 274: SNMP Information Poll Process
The basic SNMP information polling process involves a simple exchange of a GetRequest-PDU sent by an SNMP manager and a Response-PDU returned by an SNMP agent.
|
The Response-PDU message is called GetResponse-PDU in SNMPv1. Presumably, this name was chosen from the fact that it was a response to a get operation, to make the names GetRequest-PDU and GetResponse-PDU somewhat symmetric. The problem is that this name is confusing, for two reasons. First, it sounds to some people like the purpose of the PDU is to “get a response”. Second, the GetResponse-PDU was also defined as the response message for operations other than “gets”, including the reply message for SetRequest-PDU. Having a “GetResponse” message be sent in reply to a “SetRequest” is disconcerting; the new name is more generic and avoids these problems.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: The most basic type of communication in SNMP is an information poll, which allows a network management station to read one or more MIB objects from a managed node using a simple request/reply message exchange.
Key Concept: The most basic type of communication in SNMP is an information poll, which allows a network management station to read one or more MIB objects from a managed node using a simple request/reply message exchange.